How Long Does Hantavirus Live On Surfaces? The simple answer is that, while the danger of catching the disease from ancient mouse droppings is typically regarded as minimal, hantavirus can conceivably survive in them. Despite the fact that the virus doesn’t live long outside of a host, it’s important to know what circumstances impact its survivability and what measures to take while dealing with rodent infestations. This article explores the specifics of hantavirus and its prevalence in ancient droppings, giving you the information you need to safeguard your family and yourself.
Survival of Hantavirus in Droppings
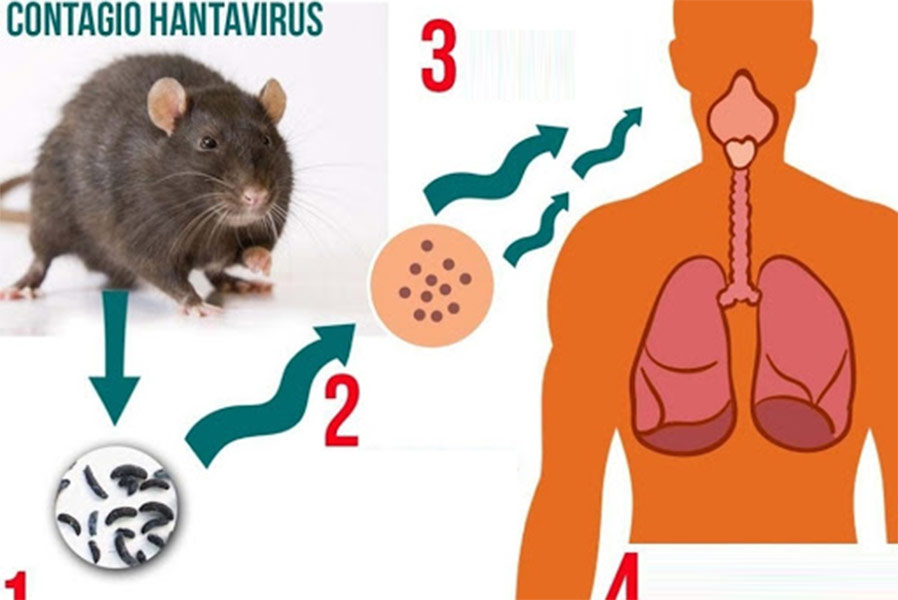
A class of viruses known as hantaviruses is spread by rodents, especially deer mice in North America. Inhaling aerosols tainted with rodent urine, saliva, or droppings is the main way that the virus is spread to people. Usually, when these materials are disturbed, microscopic particles containing viruses are released into the atmosphere.
Viability at Room Temperature: At room temperature, hantavirus may live in rodent droppings for two to three days. Numerous environmental conditions might affect its survival time.
Effect of sunshine: The hantavirus becomes less viable when exposed to sunshine. The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays have the ability to degrade virus particles, reducing the amount of time they can spread.
Cold Temperatures: On the other hand, cold temperatures may actually lengthen the hantavirus’s life period. The virus can survive longer in a frozen condition, even if it might not be active in the same way. The virus has the potential to reactivate and become harmful when temperatures rise.
Dry Droppings: Although hantavirus is seldom contracted via dry droppings, it is possible and should always be avoided.
Why Concerns About Old Droppings Persist
Old droppings can still be dangerous even if the virus has a low chance of surviving. This is the reason:
- Disturbance: Virus particles can be released into the air by cleaning or disturbing old droppings, even if they appear to be dried off. These aerosols can be produced by walking over infected regions, vacuuming, or even sweeping.
- Contamination: Old droppings may include mold, which grows well in organic, wet conditions, and other health risks even if the virus is not contagious.
- Disease Carriers: Other bacterial illnesses and allergies that might injure people can be spread by mouse droppings.
Understanding the Dangers of Hantavirus
Despite the low incidence of hantavirus infections, it is important to recognize their potential severity.
- Rare but Serious: Less than five instances of hantavirus infections are documented each year in certain places, making them comparatively uncommon. The illness, though, can be serious and even lethal.
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS): This lung infection is the most dangerous type of hantavirus infection and can result in severe respiratory distress.
- Death Rate: The significance of prophylactic actions is highlighted by the fact that the death rate from severe HPS can reach 40–50%.